Title: From ARPANET to Web 3.0: A Journey Through the Evolution of the Internet
Introduction:
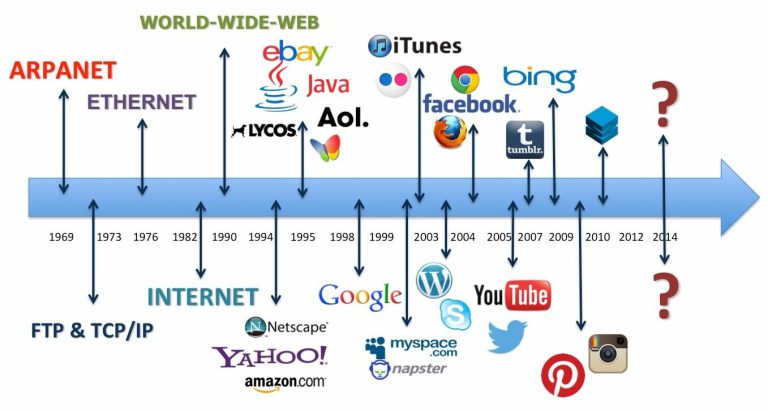
The internet has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception, starting from the early days of ARPANET to the futuristic concept of Web 3.0. This blog takes you on an immersive journey through the stages of Internet evolution, shedding light on significant milestones and technological advancements that have shaped the Internet as we know it today.
1. The Birth of ARPANET:
- In the late 1960s, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense developed ARPANET. Initially conceived as a network to connect various research institutions, ARPANET became the precursor to the modern internet. It utilized packet-switching technology to transmit data, allowing multiple computers to communicate with each other, thereby laying the foundation for the interconnectedness of the internet.
2. TCP/IP and the Birth of the Internet Protocol Suite:
- In the 1970s, the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) was developed, providing a standardized set of rules for data transmission and communication across diverse networks. TCP/IP became the backbone of the internet, ensuring seamless connectivity and data transfer between different computers and networks. Its versatility and robustness made it the fundamental communication protocol that allowed the Internet to expand globally.
3. The Emergence of the World Wide Web (Web 1.0):
- In the late 1980s, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist, invented the World Wide Web (WWW) while working at CERN. The WWW revolutionized the internet by introducing a user-friendly interface that allowed people to access and navigate information easily. Web 1.0 was characterized by static websites containing text and images, and users primarily consumed information passively. It facilitated the dissemination of knowledge and created new possibilities for collaboration and research.
4. The Dot-Com Boom and Web 2.0:
- The 1990s witnessed a massive surge in internet-based businesses, commonly known as the dot-com boom. Numerous companies invested heavily in creating online platforms and services. This era also marked the emergence of Web 2.0, a term coined by Tim O’Reilly in 2004. Web 2.0 revolutionized the internet by introducing interactivity and user-generated content. Websites became more dynamic, enabling users to actively participate, share information, and collaborate. Social media platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter gained prominence, transforming the way people connected and communicated online.
5. Mobile Internet and the Rise of Apps:
- The early 2000s witnessed a significant shift with the advent of smartphones and mobile internet. Mobile devices, led by innovations like the iPhone, brought the internet into the palms of people’s hands. Mobile apps emerged as a powerful medium, revolutionizing industries and creating new avenues for communication, entertainment, and commerce. The App Store and Google Play Store became gateways to a vast array of applications, enabling users to personalize their online experiences and access services on the go.
6. Cloud Computing and Big Data:
- The late 2000s saw the rise of cloud computing, a paradigm shift in the way computing resources were provisioned and utilized. Cloud computing enabled users to store and access data remotely through internet-connected servers, reducing the reliance on local infrastructure. This technology provided scalable computing power and storage capacity, making it easier and more cost-effective for businesses to deploy and manage applications. Additionally, the explosion of data generated by users and organizations led to the rise of big data analytics, which leverages massive datasets to extract insights, improve decision-making, and enhance personalized experiences on the internet.
7. Internet of Things (IoT) and Connectivity:
- The Internet expanded beyond traditional devices with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT refers to the interconnection of everyday objects, ranging from household appliances and wearables to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles. These interconnected devices communicate with each other and exchange data through the internet, enabling automation, real-time monitoring, and advanced analytics. IoT has transformed industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and convenience.
8. Blockchain and Web 3.0:
- As we approach the present day, the concept of Web 3.0 has emerged, envisioning a more decentralized, secure, and user-centric Internet. At the heart of Web 3.0 is blockchain technology, which provides transparent, tamper-proof, and decentralized systems. Blockchain enables secure transactions, eliminates the need for intermediaries, and promotes trust and transparency in various online interactions. Web 3.0 aims to give users greater control over their data, privacy, and digital identities, while also fostering collaboration and innovation on a global scale.
9. Artificial Intelligence and the Future of the Internet:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to become a driving force behind the future evolution of the internet. Machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and computer vision enable intelligent automation, personalized experiences, and predictive analytics. AI-powered virtual assistants, chatbots, and recommendation systems are already transforming the way we interact with the internet. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment.
10. Quantum Computing and Beyond:
- Looking ahead, the internet’s evolution is poised to be further propelled by emerging technologies such as quantum computing. Quantum computing holds the promise of exponentially faster computation and the ability to solve complex problems that are currently beyond the capabilities of classical computers. This advancement may revolutionize fields like cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery. Moreover, as technology continues to advance, the internet will continue to evolve and adapt, shaping our future in ways we can only begin to imagine.
Conclusion:
The internet has come a long way since the days of ARPANET. It has evolved from a network primarily used by researchers to a global phenomenon that impacts nearly every aspect of our lives. Each stage of its evolution has brought new opportunities, transforming the way we communicate, work, and access information. Looking ahead, the concept of Web 3.0, driven by blockchain, AI, and other emerging technologies, promises to create a more decentralized, secure, and user-centric Internet ecosystem. The journey of the internet is far from over, and the next chapter is bound to be even more exciting and transformative. As we embrace these advancements, we must also consider the ethical and societal implications to ensure that the internet remains a force for good and empowers individuals and communities worldwide.